Sign up to receive accounting tips, videos, news and webinar info before anyone else
Mailing Address
21750 Hardy Oak Blvd
Ste 104 PMB 63328
San Antonio, TX 78258-4946
(760) 697-1033
If you want to be successful in business, you need to master the art of inventory management. Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO) and other key performance indicators can shed light on a company’s health and stability.
One financial metric that tracks how long it takes for a company to sell all of its inventory is the DIO. It reveals how efficiently a business controls its stock and how fast it can transform that stock into revenue.
DIO is a metric that shows how long it typically takes for a company to sell all of its inventory, giving insight into its efficiency. You measure the frequency of inventory turnover by calculating how many times inventory is sold and replaced within a specific time frame.
There are three easy steps in learning how to calculate Days Inventory Outstanding:
This is the inventory days outstanding formula:
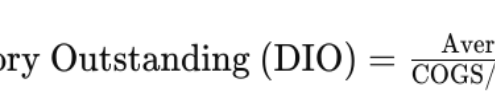
To get a better DIO, work on handling your inventory better. Set up just-in-time inventory systems to cut down on extra stock, improve the accuracy of your demand forecasts, and build smart relationships with your suppliers to make sure deliveries happen on time.
Invest in inventory management tools to keep track of and analyze stock levels easily, and streamline production processes to cut down on lead times. Review and change your inventory policies regularly to keep up with changing market wants and business requirements.
What are the factors that can affect DIO?
DIO can be affected by many things, such as changes in the demand for its goods, problems in the supply chain, outdated inventory, production delays, and new pricing strategies.
How does DIO differ from other inventory management metrics?
DIO in finance is all about the time it takes to sell inventory, while other business metrics like inventory turnover ratio track how often inventory is sold and restocked. DIO offers a perspective on inventory management that emphasizes the importance of time.
What is a good DIO benchmark?
There is no one-size-fits-all ideal DIO, as it can differ depending on the industry and the company. Typically, it’s better to have lower DIO values because they show that inventory management is efficient. However, it’s important to compare DIO with industry benchmarks and historical performance for a more meaningful analysis.
How can a company improve its DIO?
To boost their DIO, businesses can enhance their inventory forecasting methods, optimize their inventory levels, shorten supply chain lead times, adopt JIT inventory systems, and refine their demand planning procedures.
Is DIO the only metric to consider for inventory management?
No. It’s also important to consider other inventory management metrics like inventory turnover ratio, days sales of inventory (DSI), and inventory-to-sales ratio to get a complete picture of inventory performance.
Can DIO vary seasonally?
In addition to fluctuations in demand, production schedules, and inventory levels, DIO might fluctuate seasonally. When evaluating DIO trends and performance, companies need to take seasonal fluctuations into consideration.
How often should DIO be monitored?
To track changes in inventory management efficiency and identify areas for improvement, DIO should be monitored often, usually monthly or quarterly.

 Our Guide to Automation in Accounting
Our Guide to Automation in Accounting